There is neither an rda or an ai for – There is neither an RDA nor an AI for, a thought-provoking concept that challenges the current landscape of healthcare data analysis. This absence presents both challenges and opportunities, as we explore the implications and seek alternative approaches to harness the power of data for improved patient care.
The absence of RDA (Research Data Alliance) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) in healthcare data analysis raises concerns about the potential loss of valuable insights and the inability to fully leverage data for personalized medicine, disease prevention, and efficient resource allocation.
Absence of RDA and AI
RDA (Research Data Alliance) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) play crucial roles in healthcare and data analysis. RDA facilitates data sharing and interoperability, while AI enhances data processing and analysis capabilities. Their absence can significantly impact research and healthcare practices.
Without RDA, researchers face challenges in accessing and sharing data, hindering collaboration and reproducibility. Data inconsistencies and lack of standardization can lead to erroneous analysis and impede the progress of scientific discovery.
Implications for Data Analysis
- Limited data availability and accessibility hinder comprehensive analysis and informed decision-making.
- Data inconsistency and lack of standardization lead to unreliable results and difficulty in comparing findings.
- Absence of AI-driven data processing tools slows down analysis, reducing efficiency and hindering timely insights.
Examples of RDA and AI Benefits
- RDA enables data sharing across institutions, facilitating multi-center research studies and global collaboration.
- AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets, identifying patterns and correlations that would be difficult to detect manually.
- AI-powered predictive models enhance patient care by forecasting disease risks and optimizing treatment plans.
Alternative Approaches: There Is Neither An Rda Or An Ai For
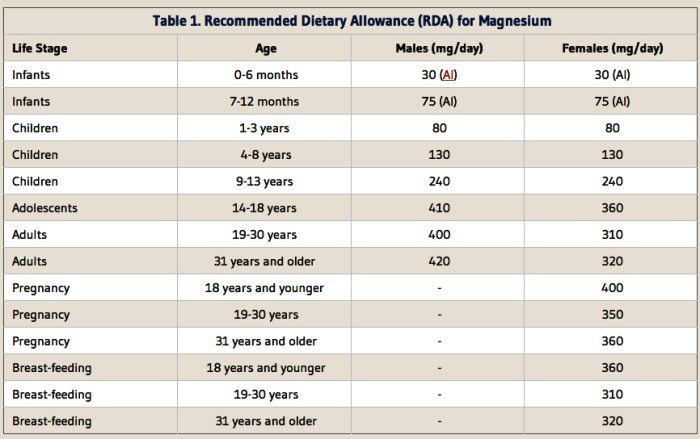
In the absence of established RDAs and AIs, alternative approaches can provide valuable insights and guidance for nutrient intake. These methods may rely on different principles and methodologies, offering unique advantages and disadvantages.
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)
DRIs are a set of nutrient recommendations developed by national and international health organizations. They include Estimated Average Requirements (EARs), Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs), Adequate Intakes (AIs), and Tolerable Upper Intake Levels (ULs). DRIs are based on scientific evidence and aim to meet the nutritional needs of healthy individuals.
While RDAs and AIs are specific intake targets, EARs represent the average daily intake that meets the needs of half of the healthy population.
Advantages:
- Established by reputable health organizations.
- Based on extensive scientific research.
- Provide a comprehensive set of nutrient recommendations.
Disadvantages:
- May not be applicable to all individuals due to variations in metabolism and nutrient requirements.
- Can be outdated as new scientific evidence emerges.
Empirical Data-Based Approaches, There is neither an rda or an ai for
These approaches rely on observational data and statistical analysis to determine nutrient intake patterns associated with optimal health outcomes. They involve studying large populations and identifying dietary patterns or nutrient intakes that correlate with reduced risk of chronic diseases or improved health status.
Advantages:
- Based on real-world data, reflecting actual dietary patterns.
- Can identify dietary patterns that promote health and longevity.
Disadvantages:
- Observational studies cannot establish causality.
- May be influenced by confounding factors and biases.
Food-Based Dietary Guidelines
These guidelines focus on promoting the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods and limiting the intake of unhealthy foods and beverages. They provide practical advice on food choices and meal planning, rather than specific nutrient intake targets.
Advantages:
- Emphasize the importance of overall dietary patterns.
- Promote healthy eating habits and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Disadvantages:
- May not provide specific nutrient intake recommendations.
- Can be challenging to follow for individuals with specific dietary needs.
Impact on Healthcare
The absence of RDA and AI in healthcare can have significant implications for patient care and healthcare outcomes. Without these technologies, healthcare providers face challenges in delivering personalized and evidence-based care.
One of the main challenges is the inability to accurately assess individual nutritional needs. Without RDA and AI, healthcare providers rely on general recommendations and population-based data, which may not account for individual variations in metabolism, activity levels, and health conditions.
Missed Opportunities for Personalized Care
- Inaccurate assessment of nutritional needs can lead to over- or under-nutrition, both of which can have detrimental health effects.
- Personalized nutrition plans, tailored to individual needs, can help prevent chronic diseases, improve overall health, and enhance recovery from illness.
Challenges in Evidence-Based Practice
- Without RDA and AI, healthcare providers lack specific targets for nutrient intake. This makes it difficult to evaluate the effectiveness of nutrition interventions and compare outcomes across different populations.
- Evidence-based practice relies on reliable data to inform clinical decision-making. The absence of RDA and AI creates a gap in this data, hindering the advancement of nutrition science.
Areas for Improvement
- Disease Prevention:Personalized nutrition plans can help prevent chronic diseases by addressing individual risk factors and promoting healthy eating habits.
- Health Promotion:RDA and AI can guide healthcare providers in developing nutrition recommendations that support optimal health and well-being.
- Disease Management:Evidence-based nutrition interventions can help manage chronic diseases, such as diabetes and heart disease, by providing tailored recommendations that address specific nutritional needs.
Future Considerations

As technology advances, we can anticipate significant developments in healthcare data analysis. RDA and AI are poised to play a transformative role, shaping the future of healthcare by enhancing disease diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient outcomes.
The integration of RDA and AI into healthcare systems holds immense potential for improving healthcare delivery. Future research and development efforts should focus on developing innovative algorithms and tools that leverage these technologies to address pressing healthcare challenges.
Role of RDA and AI in Future Healthcare
- Enhanced Disease Diagnosis:RDA and AI can facilitate the early detection of diseases by analyzing vast amounts of patient data, including electronic health records, medical images, and genomic information. This enables healthcare professionals to make more informed diagnoses and initiate timely interventions.
- Personalized Treatment Planning:RDA and AI can help tailor treatment plans to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup, medical history, and lifestyle factors. By analyzing patient-specific data, healthcare providers can determine the most effective treatment options, reducing trial-and-error approaches and improving patient outcomes.
- Improved Patient Outcomes:RDA and AI can contribute to better patient outcomes by monitoring patient health in real-time, predicting potential complications, and providing personalized recommendations for disease management. This empowers patients to take an active role in their healthcare and make informed decisions.
Research and Development Areas
- Algorithm Development:Ongoing research is crucial to develop advanced algorithms that can effectively analyze complex healthcare data and extract meaningful insights. This includes machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing techniques.
- Data Integration:Future efforts should focus on developing methods to seamlessly integrate data from various sources, such as electronic health records, medical devices, and patient-generated data. This will enable a more comprehensive analysis of patient information.
- Ethical Considerations:As RDA and AI become more prevalent in healthcare, it is essential to address ethical considerations, including data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential impact on healthcare professionals’ roles.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the significance of RDA and AI in healthcare data analysis?
RDA and AI play a crucial role in facilitating data sharing, harmonization, and analysis, enabling researchers and clinicians to extract meaningful insights from vast and complex healthcare datasets.
What are the potential implications of not having RDA or AI available?
The absence of RDA and AI limits the ability to effectively manage and analyze healthcare data, potentially hindering advancements in personalized medicine, disease prevention, and efficient resource allocation.
What alternative approaches can be used in place of RDA and AI?
Alternative approaches include advanced analytics, machine learning, and statistical modeling, which can provide valuable insights from healthcare data, although they may not fully replicate the capabilities of RDA and AI.
