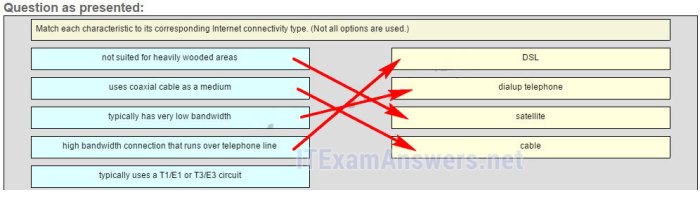
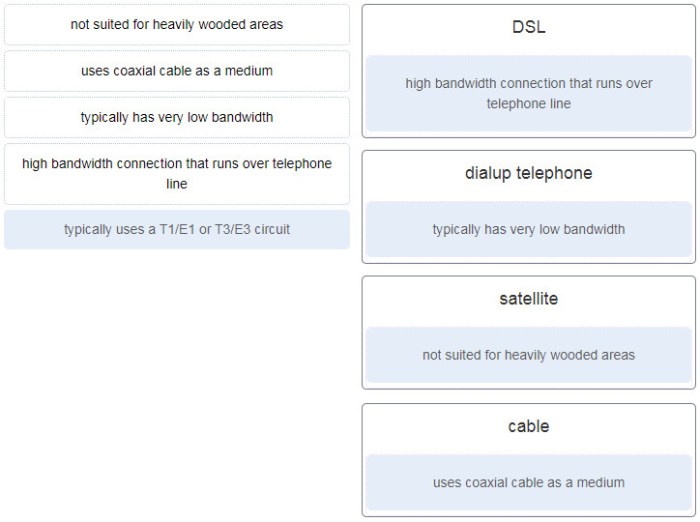
Match each lcd type with the corresponding benefit or characteristic. – In the realm of display technologies, liquid crystal displays (LCDs) reign supreme, offering a diverse range of options tailored to specific applications. This article embarks on an in-depth exploration of various LCD types, meticulously matching each with its corresponding benefits and characteristics.
Delve into the intricacies of TN, IPS, VA, PLS, and OLED LCDs, unraveling their unique attributes and identifying their optimal use cases.
As we navigate the technological landscape, understanding the nuances of different LCD types becomes paramount. Each type possesses distinct advantages and drawbacks, making it essential to discern the most suitable option for a given application. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the intricacies of LCD technology, empowering you to make informed decisions and optimize your display experience.
LCD Technology: Understanding Different Types and Their Applications
Liquid crystal displays (LCDs) have become ubiquitous in our daily lives, powering everything from smartphones and laptops to televisions and monitors. Understanding the different types of LCDs and their unique characteristics is crucial for making informed decisions when selecting devices for specific applications.
TN (Twisted Nematic) LCD
TN LCDs are the most basic type of LCD, utilizing a simple twisted nematic liquid crystal structure. When an electric field is applied, the liquid crystals align themselves, allowing light to pass through and display an image.
Advantages:
- Low production cost
- Fast response time
- Wide availability
Disadvantages:
- Narrow viewing angles
- Limited color accuracy
- Lower contrast ratio
TN LCDs are commonly used in budget-friendly devices and applications where cost and response time are prioritized, such as entry-level monitors and gaming displays.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) LCD
IPS LCDs employ a more advanced in-plane switching technology, where the liquid crystals move parallel to the display surface. This results in improved viewing angles and color accuracy.
Advantages:
- Wide viewing angles
- Excellent color reproduction
- High contrast ratio
Disadvantages:
- Slower response time compared to TN LCDs
- Higher production cost
IPS LCDs are ideal for applications where color accuracy and viewing angles are crucial, such as professional monitors, photo editing, and graphic design.
VA (Vertical Alignment) LCD
VA LCDs utilize a vertical alignment structure, where the liquid crystals are aligned vertically when no electric field is applied. When an electric field is applied, the crystals tilt, allowing light to pass through.
Advantages:
- High contrast ratio
- Wide color gamut
- Improved viewing angles compared to TN LCDs
Disadvantages:
- Slower response time compared to TN and IPS LCDs
- Narrower viewing angles than IPS LCDs
VA LCDs are suitable for applications requiring high contrast and wide color reproduction, such as home entertainment and curved displays.
PLS (Plane-to-Line Switching) LCD
PLS LCDs are similar to IPS LCDs, utilizing a plane-to-line switching technology. The liquid crystals are aligned parallel to the display surface, resulting in wide viewing angles and improved color reproduction.
Advantages:
- Wide viewing angles
- Excellent color reproduction
- Fast response time comparable to TN LCDs
Disadvantages:
- Higher production cost than TN LCDs
- Lower contrast ratio compared to VA LCDs
PLS LCDs are commonly found in high-end laptops, gaming monitors, and professional displays that require a combination of wide viewing angles, fast response time, and accurate color reproduction.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) LCD, Match each lcd type with the corresponding benefit or characteristic.
OLED LCDs are a unique type of display that utilizes organic light-emitting diodes. Each pixel in an OLED display emits its own light, eliminating the need for a backlight.
Advantages:
- Excellent color accuracy and contrast ratio
- Wide viewing angles
- Thin and flexible displays
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost than other LCD types
- Shorter lifespan compared to some LCDs
- Susceptibility to burn-in
OLED LCDs are commonly used in high-end smartphones, televisions, and monitors, offering exceptional image quality and a unique viewing experience.
Frequently Asked Questions: Match Each Lcd Type With The Corresponding Benefit Or Characteristic.
What are the key differences between TN, IPS, VA, PLS, and OLED LCDs?
TN LCDs offer fast response times and low cost, IPS LCDs excel in color accuracy and viewing angles, VA LCDs provide high contrast ratios, PLS LCDs combine the advantages of IPS and VA LCDs, and OLED LCDs boast exceptional color gamut, contrast ratio, and power efficiency.
Which LCD type is best suited for gaming?
TN LCDs with their rapid response times are ideal for fast-paced gaming, while IPS LCDs with their wider viewing angles are preferred for immersive gaming experiences.
What is the most energy-efficient LCD type?
OLED LCDs consume significantly less power than other LCD types, making them a great choice for portable devices and applications where battery life is a concern.