Circles in the coordinate plane quiz is an essential tool for students and educators alike, providing a comprehensive assessment of one’s understanding of circles and their properties. This quiz covers a wide range of topics, from basic circle concepts to advanced theorems and constructions.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Circle Basics
A circle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that is defined as the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point, called the center.
The components of a circle include:
- Center:The fixed point from which all points on the circle are equidistant.
- Radius:The distance from the center to any point on the circle.
- Diameter:The distance across the circle passing through the center, equal to twice the radius.
Equation of a Circle
The equation of a circle with center (h, k) and radius r is given by:
(x
- h)^2 + (y
- k)^2 = r^2
where (x, y) represents any point on the circle.
Circles in the Coordinate Plane
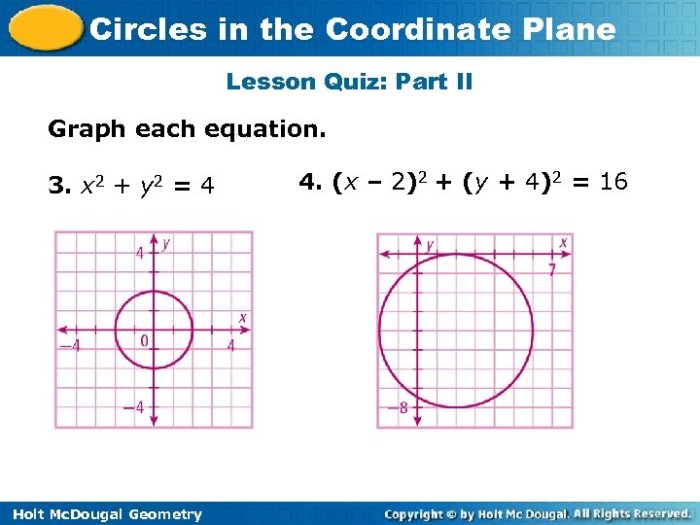
Circles are important geometric shapes with many applications in real life. In mathematics, circles can be represented and graphed in the coordinate plane using their equations.
To graph a circle in the coordinate plane, we need to know its center and radius. The center of a circle is the point (h, k), and the radius is the distance from the center to any point on the circle.
Equation of a Circle
The equation of a circle in the coordinate plane is given by:
(x
- h)² + (y
- k)² = r²
where (h, k) is the center of the circle and r is the radius.
Examples of Circles Graphed in the Coordinate Plane
- The circle with center (0, 0) and radius 2 has the equation x² + y² = 4.
- The circle with center (2, 3) and radius 5 has the equation (x – 2)² + (y – 3)² = 25.
- The circle with center (-1, 4) and radius 1 has the equation (x + 1)² + (y – 4)² = 1.
Circle Properties: Circles In The Coordinate Plane Quiz
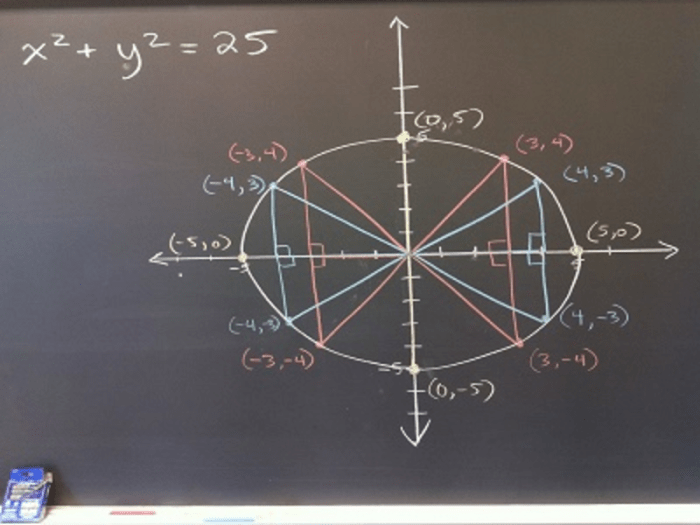
Circles possess unique properties that define their shape and behavior. These properties include symmetry, congruence, and similarity, which govern their geometric relationships. Additionally, understanding the area and circumference of a circle is crucial for various applications.
Symmetry
Circles exhibit radial symmetry, meaning they can be rotated about their center point by any angle and still appear the same. This property arises from the equidistance of all points on the circle from the center.
Congruence and Similarity, Circles in the coordinate plane quiz
Circles are congruent if they have the same radius. Congruent circles can be superimposed on each other perfectly, with all corresponding points coinciding. Similarity, on the other hand, refers to circles having the same shape but not necessarily the same size.
Similar circles have their radii proportional to each other.
Area and Circumference
The area of a circle is given by the formula A = πr², where r is the radius. The circumference, or perimeter, of a circle is calculated using the formula C = 2πr. These formulas are essential for determining the space occupied by a circle and its boundary length.
Real-World Applications
Circle properties find numerous applications in real-world scenarios. For instance, in architecture, circles are used to design domes and arches due to their structural stability and aesthetic appeal. In engineering, circles are employed in the design of gears, bearings, and wheels.
Moreover, circles play a vital role in astronomy, navigation, and various scientific fields.
Circle Theorems
Circle theorems are geometric theorems that relate to the properties of circles. These theorems can be used to solve a variety of problems involving circles, such as finding the length of a chord, the area of a sector, or the volume of a sphere.
Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
a2+ b 2= c 2
This theorem can be used to prove a number of other theorems about circles, such as the Circle Tangent Theorem and the Intersecting Chords Theorem.
Circle Tangent Theorem
The Circle Tangent Theorem states that if a line is tangent to a circle, then the square of the length of the tangent is equal to the product of the lengths of the two segments of the secant line that passes through the point of tangency.
d2= bc
This theorem can be used to find the length of a tangent line or the length of a secant line.
Intersecting Chords Theorem
The Intersecting Chords Theorem states that if two chords intersect inside a circle, then the product of the lengths of the two segments of one chord is equal to the product of the lengths of the two segments of the other chord.
AE
- EC = BD
- DC
This theorem can be used to find the length of a chord or the length of a segment of a chord.
Circle Constructions
Circle constructions involve creating circles using specific geometric tools and techniques. One common method is using a compass and straightedge.
Constructing a Circle with Compass and Straightedge
To construct a circle with a given radius “r”:
- Place the compass point at the center of the circle.
- Adjust the compass to the desired radius “r”.
- Hold the compass steady and rotate it 360 degrees to draw the circle.
Constructing a Circle Inscribed in a Triangle
An inscribed circle touches all three sides of a triangle. To construct it:
- Find the perpendicular bisectors of each side of the triangle.
- The point where the perpendicular bisectors intersect is the center of the inscribed circle.
- Use the compass to draw the circle with the center at this point and radius equal to the distance from the center to any side.
Examples in Geometric Proofs
Circle constructions are used in various geometric proofs. For instance, to prove that the angle inscribed in a semicircle is a right angle, construct a circle with the diameter as the base of the angle and the vertex on the circle.
The inscribed angle will be 90 degrees.
Question Bank
What is the equation of a circle?
The equation of a circle with center (h, k) and radius r is (x – h)^2 + (y – k)^2 = r^2.
How do you find the area of a circle?
The area of a circle with radius r is πr^2.
How do you construct a circle using a compass and straightedge?
To construct a circle using a compass and straightedge, follow these steps:
- Draw a line segment of the desired length.
- Place the compass point on one endpoint of the line segment.
- Adjust the compass to the desired radius.
- Draw an arc that intersects the line segment at two points.
- Connect the two points to complete the circle.